






Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (ESC) is also increasingly preferred in lacrimal sac drainage operations (Dacriocystorhinostomy) and surgical treatment of pituitary gland adenomas (Endoscopic hypophysectomy) due to its advantage of minimal surgical trauma.
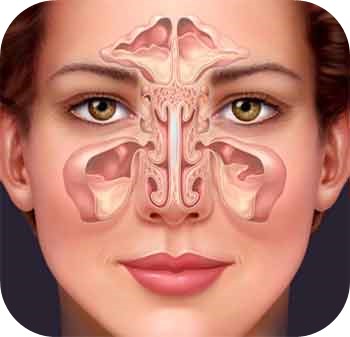
The narrow areas of the sinuses around the nose, the complexity of the anatomy, and the proximity of important organs such as the brain, eyes, optic nerves, tear ducts, and carotid vessels require education and experience, as well as high technical skills with low margin of error in endoscopic sinus surgeries.
In this surgical application, the sinuses are reached by working through the nose with the help of an endoscope. The sinuses are cleaned without damaging the surrounding tissue, and the natural channels are opened, allowing the physiology to work regularly after the operation.
Endoscopic surgery; Since it is an operation that takes care of sinus functions and corrects impaired physiology, its results are very successful. With the help of endoscopes that show the finest details of the nose and sinuses and special microsurgical instruments, the operation with an appropriate technique and patient follow-up solves the problem of sinusitis to a large extent.

In chronic sinus diseases, ESC mainly;
* Cleaning of inflamed tissues/polyps,
* Opening of the discharge channels connecting the sinuses to the nose,
* Correction of anatomical problems such as concha bullosa, multiple discharge holes (accessory ostium), abnormal mucosal contact areas are performed.
General anesthesia is preferred for the comfort of the patient and the surgeon, especially in cases where advanced technological devices such as navigation, balloon, shaver are used during ESC. The duration of the surgery varies according to the extent of the pathology and whether there are additional interventions such as correction of nasal curvature, aesthetic nose surgery, reduction of the concha, correction of anatomical variations to be performed in the same surgery. While the intervention in a single sinus takes around 15 minutes, the clearance of the pathology involving all sinuses may take more than 2 hours.
If there is no necessity due to additional interventions such as reduction of the nasal concha, a tampon is not placed in the nose after sinus surgery, and the patients can breathe easily through the nose. At the end of the operation, special pads and various materials placed in the surgical area under the middle concha to prevent bleeding and tissue adhesions that may occur during healing do not adversely affect nasal breathing.
There is no serious pain complaint after the surgery, simple painkillers are usually sufficient.
Although it is recommended that patients stay in the hospital on the day of surgery, they can be discharged on the same day depending on the content of the surgery.
There is no serious pain complaint after the surgery, simple painkillers are usually sufficient.
Although it is recommended that patients stay in the hospital on the day of surgery, they can be discharged on the same day depending on the content of the surgery.
It is recommended to continue the antibiotic treatment for at least 10 days after the surgery, this period can be extended or additional drugs can be added when necessary. Sprays containing sterile saline, which mechanically clean the nose and moisten the mucosa, should be used until the crusts subside. In patients with allergies and polyps, cortisone-containing sprays and drugs that reduce the risk of polyp formation are started from the second week. Oral fungal treatment is also recommended after surgery for patients who are thought to have allergic fungal sinusitis.
During the first dressing in the postoperative period, the crusts formed in the nasal and sinus drainage channels are cleaned, if materials that prevent adhesion are placed in the sinus, they are removed, infection control is performed. Performing the first dressing properly is very important for the success of the surgery. Depending on the extent of the surgery, patients should come to the controls with 7 to 10-day intervals until the recovery is completed.
In ESC, in some special cases, the difficulty of the operation increases and increases the possibility of failure or complications. These special cases;
• Excessive bleeding in tissues during surgery,
• Severe inflammation,
• Operations especially for tumors with high vascular content,
• Hypertension,
• Coagulation disorders (Bleeding diathesis) / Aspirin use,
• Surgical trauma,
• Anatomy has changed due to previous surgery / trauma,
• Formation of hard healing tissue due to previous surgeries,
• Diffuse polyps,
• Tumors inside / outside the paranasal sinus,
• Anatomical changes (variations),
• Operations for posterior ethmoid, sphenoid and frontal sinuses can be counted.
There are some minor and major complications encountered during or after ESC. The most important of these are;
• Active bleeding,
• Intraorbital (intraocular) bleeding,
• Carotid (carotid artery) rupture,
• Orbital (eye socket) trauma,
• Endophthalmitis (backward displacement of the eye),
• Eye movement disorder,
• Nasolacrimal duct (tear duct) trauma,
• Cerebrospinal fluid leakage,
• intracranial complications;
o Abscess,
o Meningitis,
o Air leakage into the brain (pneumocephaly),
o It can be listed as pituitary gland damage.