
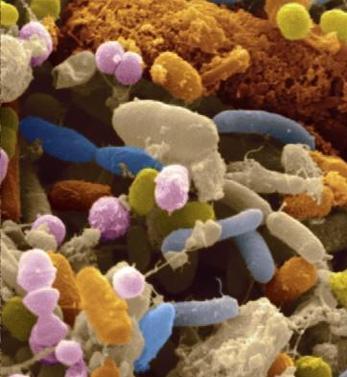
Each person is made up of about 60 trillion cells. About 30 trillion of these cells are human cells. Some 30 trillion are microorganisms living in the human body (bacterial cells are about 10 times smaller than human cells, viruses are much smaller). These harmless microorganisms, which can be viruses, bacteria or fungi, are called the microbiome / microbiota / flora and are most concentrated in the gut, then on the skin, mouth and vagina. The microbiota in the gut, on the other hand, weighs 2 kilograms and is now considered an organ because of both its function and weight. We continue to live in mutual interest with these beneficial microorganisms.
 The colon and rectum make up the part of the digestive system called the large intestine. The last 20 cm is called the rectum, and the part from here to the small intestine is called the colon. It is approximately 1.5 m long in total. Partially digested food comes from the small intestine to the colon. The colon separates water and minerals from food and stores the rest for expulsion through the anus.
The colon and rectum make up the part of the digestive system called the large intestine. The last 20 cm is called the rectum, and the part from here to the small intestine is called the colon. It is approximately 1.5 m long in total. Partially digested food comes from the small intestine to the colon. The colon separates water and minerals from food and stores the rest for expulsion through the anus.
Cancer that starts in the colon is called colon cancer, and cancer that starts in the rectum is called rectal cancer. Therefore, in general, both colon cancer and rectal cancer are called colorectal cancer together. Colon and rectal cancers develop from the cells that form the layer that covers the inner surface of these organs. According to the statistics of our country, colorectal cancer is the third most common cancer in both men and women. In other words, it is a very important health problem for our country. Colorectal cancers often do not cause any complaints or symptoms in the early stages of the disease. Colonoscopy is the most effective method for early diagnosis. Studies indicate that the examination of the intestinal microbiota will play a very important role in the evaluation of colorectal cancer. It has been determined that the colon microbiota triggers colorectal cancers by changing and multiplying epithelial cells (laying the inner surface of the intestine), bioactive product synthesis and affecting the immune system.
The main factors associated with the formation of colorectal cancers are; nutrition, genetic mutations and inflammatory bowel diseases. It is now known that nutrition is the most important triggering factor for the disease. The frequent occurrence of large bowel cancers in our country is actually one of the indicators that our diet is not very healthy.
The gut microbiota is directly affected by antibiotic use and poor eating habits and is associated with many diseases, including colorectal cancers.