







Prominent Ear Aesthetics, also known as Otoplasty, is the name given to the surgery performed to correct the appearance of the auricle.
An overly prominent auricle, which is also called prominent ear among the people, and the auricle and earlobe that are not developed or distorted due to congenital or trauma-like reasons can be corrected and reshaped by otoplasty.
Prominent ear can cause social and mental problems, especially in childhood. As they grow up, children who enter social environments such as kindergarten, kindergarten, school may be exposed to cruel reactions and criticisms due to the appearance of their ears. Being the subject of ridicule in friend circles can lead to exclusion, problems in self-confidence and personality development; It can cause communication disorders, school failure and a decrease in self-confidence. For this reason, it is generally accepted that the best time for otoplasty surgeries is preschool. Adults may also need otoplasty surgery for reasons such as getting rid of an appearance that can be perceived as a disadvantage in social environments, collecting their hair above their ears or having a short cut comfortably. Otoplasty is a very common facial plastic surgery. It can be performed under general or local anesthesia, with day surgery or a short hospital stay.
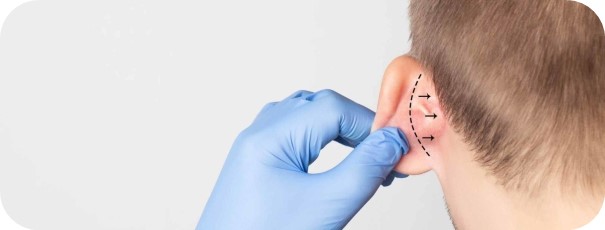
The auricle consists of a thin soft tissue and cartilage covered with skin. At the age of 5, the auricle completes its development. However, the cartilage content continues to change over the years. Cartilage, which has a softer and foldable structure in young children, becomes harder in older people. The unique shape of the auricle is the result of many folds formed during development in the womb. If some of these folds are not fully developed, prominent ears occur. As with all other facial structures, one ear is not exactly alike to the other. The aim of the surgery is to make the ears less prominent, similar in appearance and more natural.
The best pre-operative preparation can be achieved by having a candid interview where all questions will be answered fully. The doctor must understand the patient's expectations and wishes. What the patient can and cannot achieve with surgery in a clear and realistic way; Asking and learning how the ear will look after the surgery will help him determine his expectations from this surgery.
It is very important to determine the time of otoplasty surgery for children. Otoplasty is generally not recommended before the age of 5 years. However, if the surgery is delayed too long, the child may grow up with psychological problems.
High-quality photographs should be taken in order to guide the pre-operative interview, to provide the opportunity for comparison to the physician during the operation, and to compare the results obtained after the operation. If the operation is planned to be performed under general anesthesia, a separate meeting should be held between the patient or their relatives and the anesthetist.
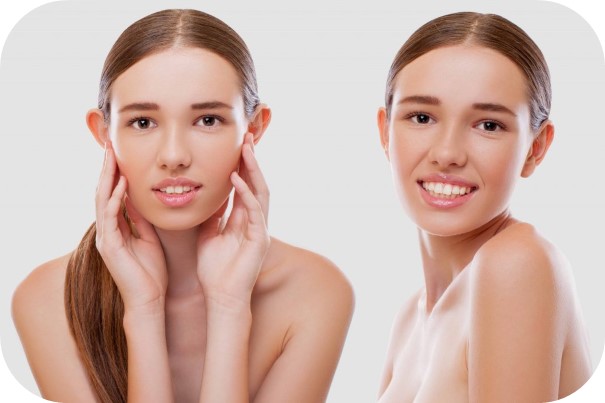

There are many different surgical techniques to correct prominent ear. In children or young patients, shaping can be done with sutures, as the cartilage flexibility is high. In order to give the desired shape to the cartilage, certain areas can be marked and folded, thinned and weakened; If there is excess cartilage or soft tissue, it can be removed. Regardless of the technique applied, an incision is made in the crease behind the ear. This incision is closed with appropriate suture materials chosen considering the aesthetic result and durability. At the end of the surgery, a dressing is applied to apply a slight pressure on the newly formed auricle.
Postoperative
As with surgical techniques, each physician may have different post-operative practices that result from their own experience. Differences in practice do not mean that one method is better than the other. However, the patient is usually seen on the first postoperative day and the dressing is changed or removed. There is usually no serious pain after surgery; Mild pain, which can be controlled with painkillers, can be expected. Headband is applied day and night for 1 week; for the next few weeks, it is desirable to wear the headband only at night. While children can start school after 1 week, adults can return to work earlier. Physical activity is restricted for 10 to 14 days and contact sports are restricted for at least 2 months. Follow-ups, which are planned more frequently in the first weeks after the surgery, are usually repeated at the 3rd and 12th months. By this time, the scar behind the ear gradually decreases. Since the incisions are behind the ear, the scar is hidden and usually does not cause cosmetic problems.