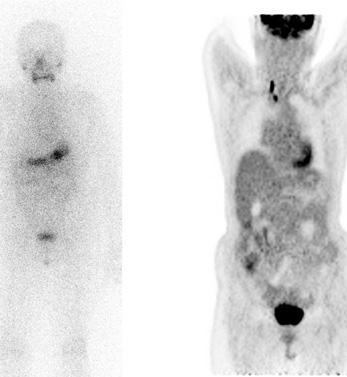
Radioactive iodine therapy, popularly known as "atom therapy", is performed following surgery in thyroid cancer. Purpose; The only treatment option is to destroy the remaining thyroid tissue, thyroid cancer cells in the lymph node or other parts of the body. With radioactive iodine treatment, the remaining tissue in the thyroid bed is removed after the operation, making the patient's follow-up easier. It also reduces recurrence and prolongs survival by demonstrating and treating occult metastases.
It has been proven by research that radioactive iodine treatment with appropriate patient selection following the correct surgical operation has completely eliminated the disease in more than 95 percent of patients.
Who is radioactive iodine treatment applied to?
Patients who will receive this treatment are determined immediately after the operation and radioactive iodine treatment can be applied approximately 3-4 weeks after the surgical operation.
It is applied in papillary and follicular carcinomas defined as differentiated thyroid cancer. The treatment is given for ablation (destroying the remaining thyroid tissue that cannot be surgically removed) and treatment to all patients with a tumor diameter of more than 1 cm. If the tumor diameter is less than 1 cm, total thyroidectomy may be sufficient, but if the tumor diameter is smaller than 1 cm, but metastasis is detected, if there is capsular invasion, if it has received radiation especially to the neck region before, or if it is in bad cell type, radioactive iodine treatment is applied.
How to prepare for radioactive iodine treatment?
The treatment is applied by increasing the TSH hormone to increase the entry of iodine-131 into the remaining thyroid and tumor cells and to increase the effectiveness of the treatment. Treatment can be applied to the patient, usually 3-4 weeks after the operation. Making a plan after the treatment so that the patient does not stay in hypothyroidism for a long time increases the comfort of the patient. A diet low in iodine for 10-15 days prior to treatment greatly increases the success of treatment. Treatment preparation stages should be planned by the nuclear medicine doctor in accordance with the patient and discussed in detail with the patient.
How is radioactive iodine therapy administered?
• On the morning of the iodine treatment, the patient comes to the hospital with a hunger for about 6 hours.
• The patient is taken to the radioactive treatment room (lead-covered) for iodine treatment by performing the necessary blood tests.
• The radioactive substance is given to the patient in the form of capsules orally.
• The patient stays in this room for 3-5 days on average, depending on the dose of medication taken.
Side effects and precautions of radioactive iodine therapy
The radioactive iodine capsule given in the treatment does not have any bad taste or smell, the patient does not feel anything during the treatment. Hair loss, which is observed in other chemotherapy methods, is not observed, and the occurrence of side effects due to the gastrointestinal system is very rare in this treatment. Some methods are recommended to the patient so that the treatment given does not damage the salivary glands. In addition, drinking plenty of water and taking a shower every day and cleaning the patient from the radiation excreted by body secretions facilitates the removal of radiation from the body. Visitors are not accepted during treatment and their needs are provided under the control of health personnel.
Duration of radioactive iodine treatment
We are aware that it is actually extremely difficult for a person to stay in a room alone for at least three days. Thanks to the system and communication established in our center, it is aimed to minimize this difficulty.