







With the "stapedectomy" operation, the stapes bone, whose movement is restricted due to otosclerosis disease, is removed and a prosthesis that will transmit sound waves to the inner ear is placed in its place. With this surgery, which can be performed under local or general anesthesia, 90-95% successful results are obtained, and conductive hearing loss can be almost completely corrected in the vast majority of patients.
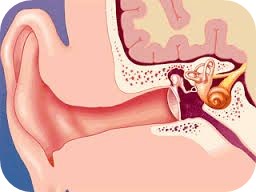
How Is Stapedectomy Performed?
Surgery is not recommended for patients with very mild conductive hearing loss or severe neurologic hearing loss where the inner ear hearing organs are severely affected. Stapedectomy surgery is recommended for all otosclerosis patients, unless there is a serious health problem that prevents surgery.
Dizziness may occur for a few days after surgery. At the end of the surgery, surgical sponges placed in the external ear canal are removed in 7-10 days, and the patients can return to their normal lives at the end of this period.
Although the risks of stapedectomy surgery performed with appropriate surgical equipment and surgical techniques are quite low, there is a risk of hearing loss of approximately 1% in every surgery performed for middle ear problems. Apart from this, complications such as the formation of a hole in the eardrum, damage to the facial nerve, infection in the ear, and early dislocation of the piston can be observed much more rarely.