
Tension-type headaches are generally thought to be caused by stress, but stress is only one of the factors that trigger the pain. In tension-type headache, it causes a feeling of pressure as if there is a band around the head. The tension type is the most common type and its causes are not yet known.
To manage this type of headache;
It is necessary for the person to acquire healthy habits, to use medication only when necessary, to cope with headaches without medication, and to manage stress well.
Tension-Type Headache Symptoms
The main symptoms of tension-type headaches are;
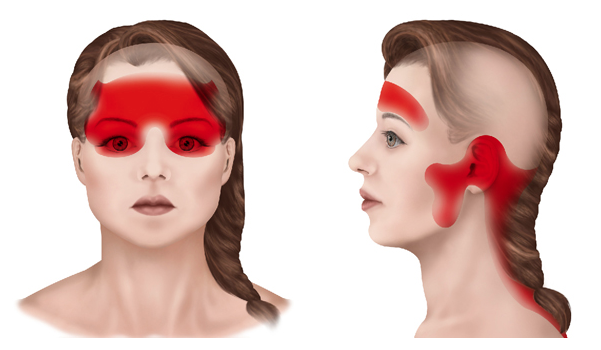
Headache with a feeling of fullness in the head, a feeling of pressure on the forehead or temples, tenderness in the scalp, neck and shoulder muscles.
Tension-type headaches are divided into two main categories, episodic and chronic;
Episodic Tension Headache
Episodic tension headaches can range from 30 minutes to a week. Frequent episodic tension headaches occur less than 15 days per month for three months. Frequent episodic tension headaches can become chronic.
Chronic Tension Headache
The pain can last for hours or be continuous. If the headache occurs on 15 or more days a month for three months, it is considered chronic tension ligament pain.
Distinction between Tension and Migraine Headache
Sometimes it can be difficult to distinguish tension-type headache from migraine. Some people may experience both migraine and tension-type headaches together.
Nausea, vomiting and visual disturbances are not found in tension headaches as in migraine. Although physical activities usually make migraine worse, tension headaches can be good as they have no effect on the pain. Similar to migraine, sensitivity to light and sound may occur, but it is not as severe as migraine.
When Should You See a Neurologist?
Tension headaches can reduce your quality of life. In this case, if you need to take medicine for headache two or more days a week, you should see a neurologist.
When to Seek Emergency Assistance?
Contact your doctor as soon as possible if a sudden severe headache, fever, stiff neck, confusion, weakness, double vision, numbness, or difficulty in speaking are accompanied by a headache that worsens and especially if it is a pain that develops after a head injury.
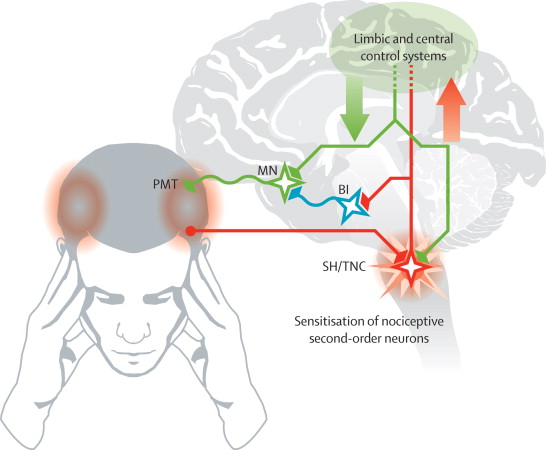
The cause of tension headache is unknown. It is thought to be caused by contractions of the facial, neck and scalp muscles as a result of increased emotional tension or stress. However, some studies do not show muscle contraction as an obvious cause.
The most common theory is that people with tension headaches have an increased sensitivity to pain. Increased muscle sensitivity and tension in the muscles are among the common symptoms. It is thought that this situation may be caused by sensitizing pain pathways.
Because tension headaches are so common, their impact on work productivity and overall quality of life is significant. Frequent pain can seriously affect your quality of life and make you reluctant to do or continue daily activities
 Diagnosis
Diagnosis
If you have chronic or recurrent headaches, after the interview and neurological examination, your doctor can determine the possible cause of your headaches:
Your doctor can learn a lot about headaches from the pain description. Be sure to include these details. Pain characteristics play an important role in the diagnosis of the disease. For example; Is your pain throbbing? Is it continuous or constant? Like sharp or stabbing?
Pain Intensity
One of the best indicators of understanding headache severity is how likely it is to work while the pain is present. Can you do your job? Does the headache wake you up or prevent you from falling asleep?
Location of Pain
Do you feel pain on just one side of your head or all over your head? Is the pain just in your forehead or behind your eyes?
Imaging Tests
If you have a headache that is suggestive of secondary headache other than tension-type headache, or if your neurological examination is impaired, your doctor may order some tests to rule out other possible serious causes.
These tests are;
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Computed tomography (CT)
Electroencephalography (EEG)
Blood biochemistry
 Tension-Type Headache Treatment
Tension-Type Headache Treatment
Lifestyle Changes
Sometimes all you need is rest, a cold application with ice packs, or a long, hot shower to relieve a tension headache. Trying a variety of methods before using medication can help reduce the severity and frequency of chronic tension headaches. You can try some of the following:
Manage Your Stress Level
Planning and organizing your busy periods ahead of time is a very good option to reduce stress. Another important point is to create time for yourself to rest, even for a short time, during these periods. If you encounter a predictable, stressful situation, you should focus on other options available to you.
Hot or Cold Application (Which You Prefer)
Applying heat or cold to the aching muscle can provide relief from tension headaches. You can use a low-temperature heating pad, a hot water bottle and a hot compress, or a hot towel.
A Hot Shower Can Also Help
In cold application, you can wrap ice in a cloth to protect your skin or use ready-made ice packs, frozen vegetable packs.
Correct Your Posture
Good posture helps your muscles contract and stretch properly. While standing, keep your shoulders back and head level. Pull the abdomen and buttocks in. While sitting, make sure your thighs are parallel to the floor and your head is upright.
Coping and Support
Living with chronic pain can be difficult. Chronic pain can make you more anxious or moody. It can seriously affect your relationships, productivity and quality of life.
Cognitive behavioral therapy can be helpful in learning to manage stress and can be effective in reducing the frequency and severity of headaches.