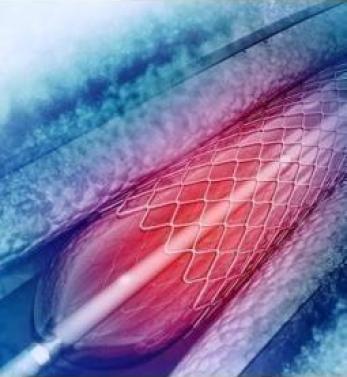
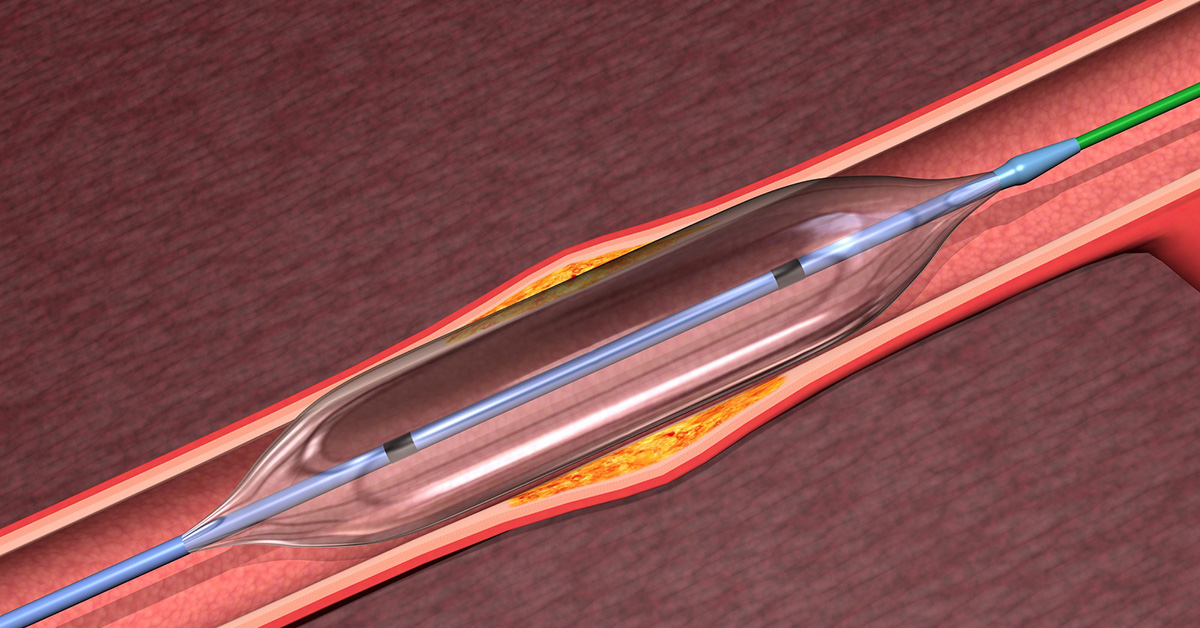
Angioplasty is a technique of mechanical widening of arteries that are narrowed or blocked, usually as a result of atherosclerosis. An empty, deflated balloon, known as a catheter, is placed in the narrowed vein above the guide wire and inflated to a fixed size using water pressure 75 to 500 times (6-20 atmospheres) greater than normal blood pressure. The balloon causes the inner white blood cell/clot plaque layer and surrounding muscle wall to expand, resulting in better flow in the blood vessel. The balloon is then deflated and removed. In some cases, a stent may be inserted to keep the vessel open.