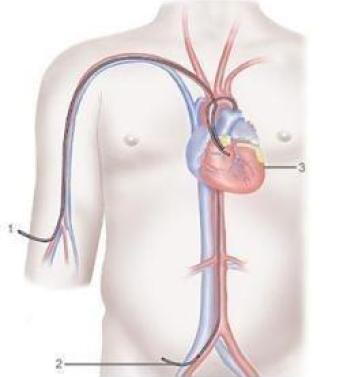
It is a method used to detect the disease of the arteries feeding the heart. It is caused by cardiovascular disease. Coronary angiography also detects how narrowed or blocked which part of the arteries feeding the heart is. It determines the stenosis or occlusions in the heart vessels and ensures that the treatment is directed as needed. Inguinal or arm arteries are used as the intervention site in coronary angiography. First, the sheath is placed on the artery at the intervention site, and the vascular structure is visualized with the opaque substance (painted substance) given to the beginning of the heart vessels by using different catheters through this sheath. Coronary angiography is performed in specially deployed angiography rooms. After the procedure is over, the sheath placed on the artery at the intervention site is removed, and the bleeding is stopped by applying pressure to that area. After the tight bandage is applied, the patient is taken to the bed. Coronary angiography is completed 20 to 30 minutes after the patient is taken to the angio room. In some cases (bypass patients, patients who have had different heart surgeries before, patients with occlusion in the inguinal or arm veins, etc.), this period may be longer. Hospitalization of the patient is required for coronary angiography. After the procedure is completed, the patient is rested for 6 hours and then he is allowed to stand up. If his general condition is suitable and his doctor approves, he is discharged. In some cases, the suture system can be used after the sheath has been removed. These patients can be discharged by standing up earlier.