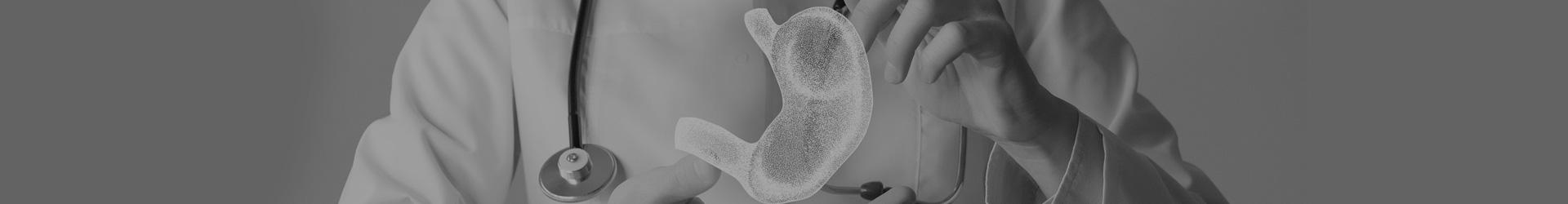
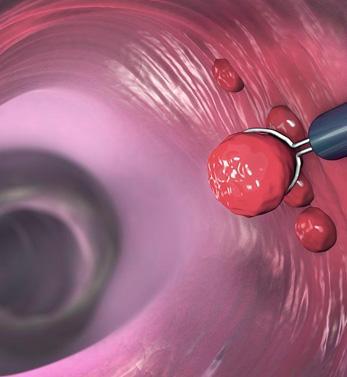
Polyps can occur in many parts of the body. They are structures formed by cells multiplying more than normal. Polyps that can occur in almost any part of the body such as the uterus, nose and stomach are also seen in the large intestine. It is important to remove the polyps that occur in the large intestine before they become cancerous. For this reason, it may be vital that people in the risk group are checked at regular intervals.
Large intestinal polyps appear as abnormal growths that rise from the lining of the intestinal tract. Intestinal polyps are usually harmless, but neglected and growing polyps can lead to more serious health problems in the future.
 WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF BOTTOM POLYP?
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF BOTTOM POLYP?
Large intestinal polyps may not cause any symptoms. Many polyps are found incidentally during routine checkups. However, the most common symptoms are;
Experiencing these symptoms does not mean that a person has colon cancer caused by polyps or polyps. Hemorrhoids or some drugs used can also give similar symptoms. It is important to consult a specialist to be sure, in order to prevent serious health problems that may occur.
WHAT ARE THE CAUSES OF BOTTOM POLYPS?
It is not known exactly why polyps occur. There are risk factors for the formation of polyps that can be seen in everyone.
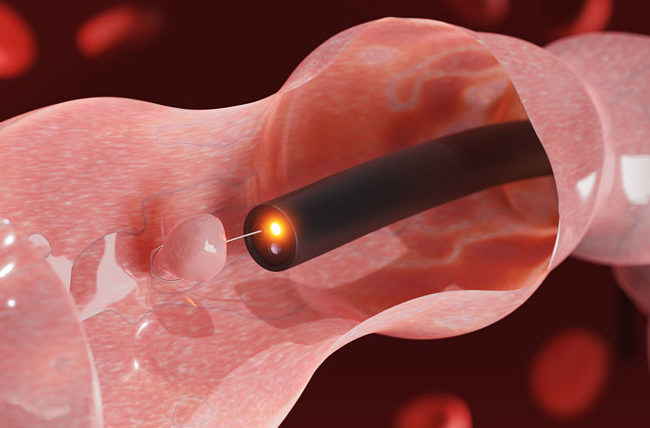
HOW ARE BOOT POLYPS DIAGNOSED?
Colon polyps can be identified in several ways. Screening tests play an important role in detecting polyps before they become cancerous.
Scan methods:
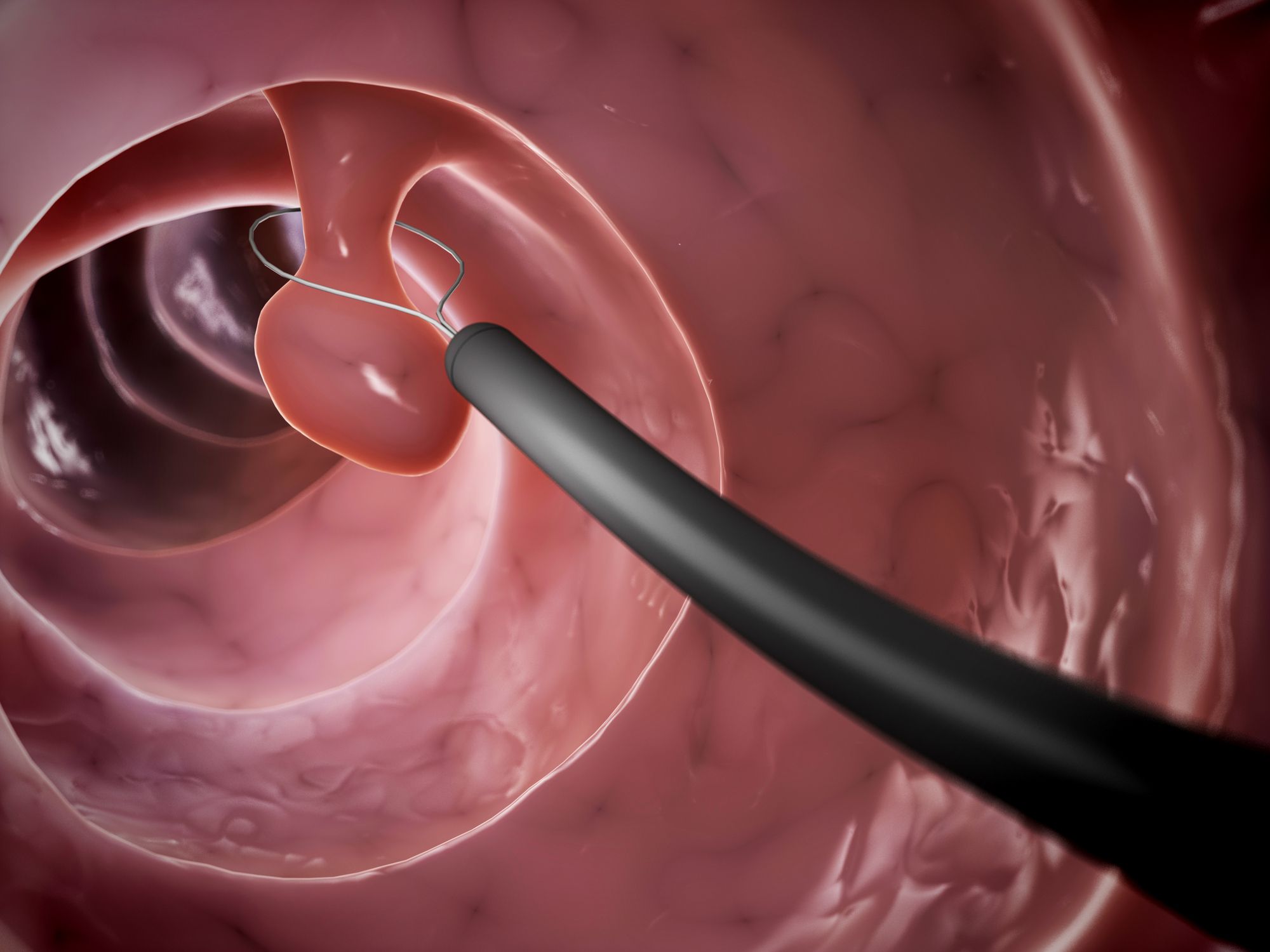
Colonoscopy: Large intestine; It is examined with a soft, pliable instrument with a camera at the end. The most sensitive test for polyp is colonoscopy. If polyps are found during the scan, they can be removed immediately by the doctor. The biopsy was abandoned by taking a tissue sample from the polyp. It is much healthier to remove the seen polyps immediately by the specialist doctor.
Virtual colonoscopy: It is performed by means of radiological imaging such as Computed Tomography (CT) or Magnetic Resonance (MR). The presence of polyps is investigated by imaging performed after the contrast agent administered into the colon. With virtual colonoscopy, there may be problems in recognizing very small polyps, and in the presence of polyps, colonoscopy will be required to remove them.
Flexible sigmoidoscopy: The presence of polyps is checked by examining the lower part of the arm and the rectum with an instrument with a light and a camera at the end.
Stool-based tests: The presence of blood in the stool is checked and the presence of polyps is examined by colonoscopy in cases where it is positive.
Barium enema: It is a method used in the diagnosis of colon polyps. Due to the development of the methods used in diagnosis with the developing technology, it is not used as often as before. Polyp diagnosis is made by X-rays by filling the large intestine with barium. However, the barium enema method has been almost abandoned due to the use of methods such as colonoscopy and virtual colonoscopy.
HOW IS THE TREATMENT OF BOTTOM POLYPS DONE?
Intestinal polyps should be removed when detected. Depending on the type and number of polyps, the procedure may vary.
Polypectomy: It is the removal of the polyp from the large intestine with forceps or wire loop. If the polyp is larger than 1 centimeter, the procedure can be performed by injecting a liquid to remove and isolate the polyp from the surrounding tissues.
Minimally invasive surgery: Polyps that are too large or cannot be safely removed during screening of the large intestine and rectum are usually removed laparoscopically.
Colon and rectum removal: In the presence of a rare inherited disease such as FAP, surgery may be required to remove your colon and rectum (total proctocolectomy). For people with such familial health problems, the best way to prevent colon cancer is to have the colon and rectum completely removed.