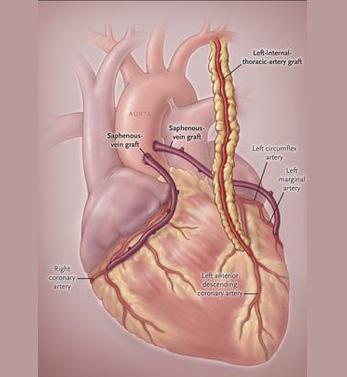




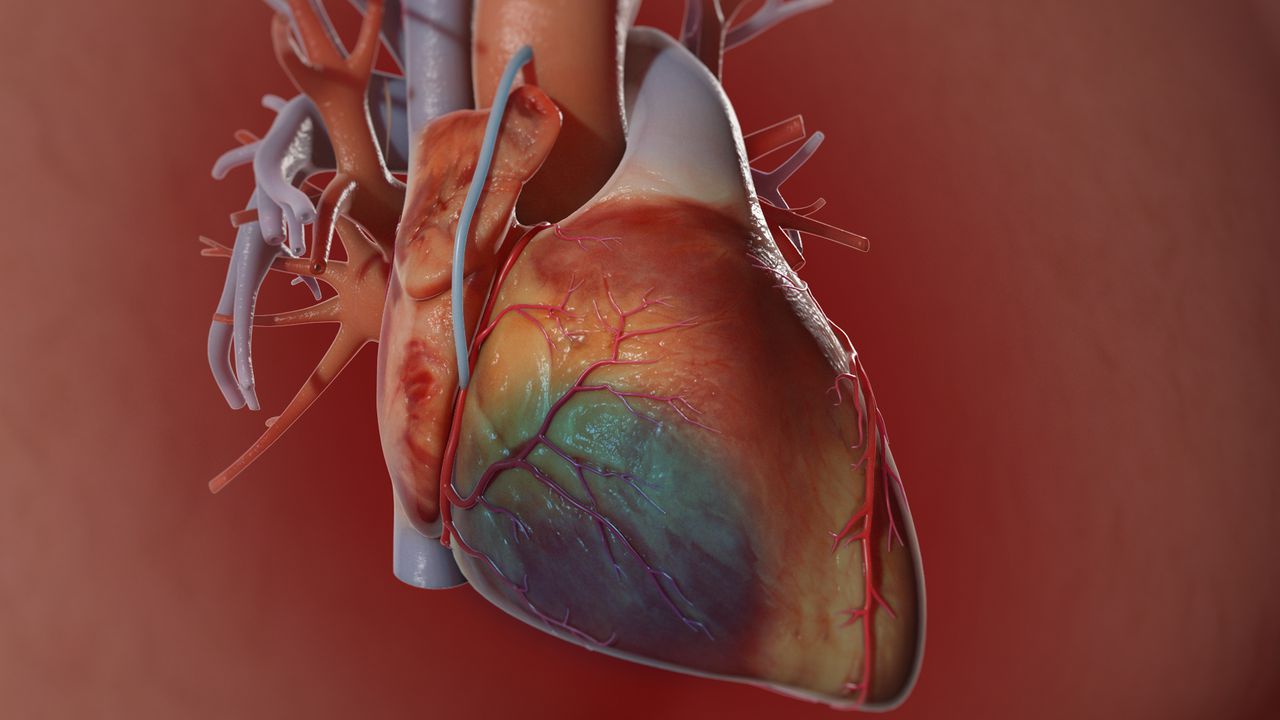
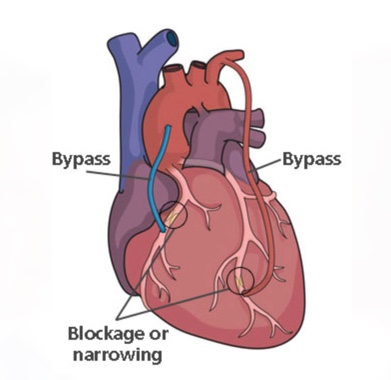
When there is a narrowing or blockage in the coronary arteries that supply the heart, the heart cannot be fed adequately and cannot perform its normal functions, and the person complains of chest pain and fatal problems such as heart attack (myocardial infarction) occur.
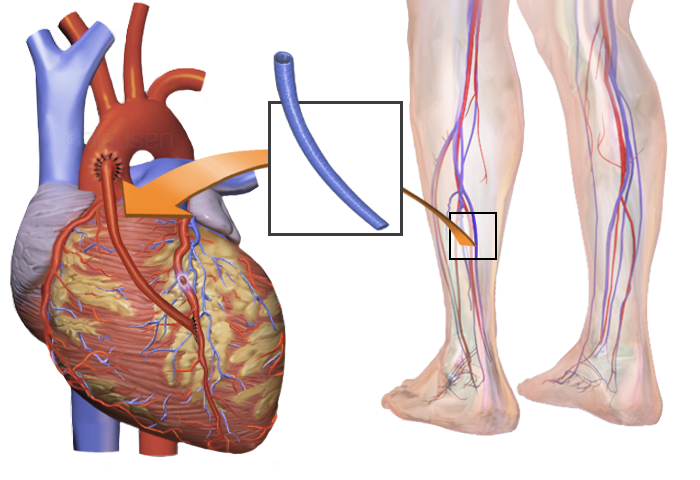
Coronary bypass surgery is a surgical intervention performed due to occlusion of the arteries (coronary) feeding the heart. For the bypass procedure, only the veins of the patient, such as the leg vein, forearm artery, and thoracic artery, taken from the patient, are used without causing loss of function at the place where they are taken, and these vessels are prepared and transferred to the patient area to restore blood circulation.
Coronary bypass surgery can be done in two ways:
Bypass in the stopped heart: While the heart is completely stopped and the circulation in the body is maintained by a heart pump, the process of bridging the vessels is performed. The heart pump takes over the duties of the patient's lungs and heart during the surgery, providing blood pumping to the brain and other vital organs.
Bypass in the working heart: Surgery is performed without stopping the heart and without the need for a heart pump. In a beating heart, the risk of infection is much lower in coronary bypass operation, and the patient's recovery and discharge are quicker. In addition, the need for blood transfusions during the operation is less and risks such as stroke can be kept low.
In addition to these methods, which are preferred according to the type of the case, the operation can also be performed with the closed surgical method, which is defined as the open or endoscopic method. After the method of coronary bypass operation is decided, the patient is anesthetized. Although coronary bypass operations are mostly performed under general anesthesia, local anesthesia may also be preferred in selected cases. The effect of the current health status of the person is great in determining the type of anesthesia. In addition to hypertension, diabetes and lung diseases, general anesthesia may not be applied to people with kidney dysfunction.
Where is the vein taken from for coronary bypass?
For the vein to be taken from the chest, the sternum is cut with the help of a bone saw and the thorax is opened. Generally, the mammary artery in the left breast is used. In the presence of more than one coronary artery that needs to be bypassed, the vein in the leg of the person or the radial artery in the arm, that is, the vein in the forearm that feeds the hand, can also be used.
For the vein to be taken from the leg, an incision is made in the leg, and the vein of sufficient length for the bypass is removed. One end of the removed vessel is sutured to the coronary artery below the occluded area. The sternum is tied with strong wires and the surgical area is sutured.
After the operation, the scar (scar) in the area where the vein is taken may be too small to be seen with the naked eye.
Who Is Bypass Applied To?
Multiple vascular disease
Inability to open more than one coronary vessel without surgery (balloon and stenting),
Conditions requiring heart valve operation,
Re-occlusion of one or more veins despite being opened with a non-surgical method,
Coronary bypass surgery is preferred if there is another heart condition that requires surgery.
How Long Does Bypass Surgery Take?
The total duration of coronary bypass surgery differs depending on whether the surgery is performed with open or closed method. In addition to the number of vessels to be bypassed, another factor affecting the duration of the operation is that the operation is performed on a working or stopped heart. Today, coronary bypass operations, which are mostly carried out with minimally invasive methods, can take approximately 3 to 6 hours. Other surgical interventions for the heart, such as the replacement of the heart valve of the person with the same operation, cause a prolongation of the operation time.
 What are the Bypass Risks?
What are the Bypass Risks?
The risk of surgery depends on demographic factors such as the patient's age, gender, lifestyle and chronic diseases.
The risk of loss of life is low in coronary bypass operations. However, factors such as the age of the person, accompanying diseases, how much of the heart muscle has been damaged due to a heart attack, and the presence of loss of function in other tissues and organs increase the risk of surgery. Patients who experience psychological trauma after the operation may need psychological support.
Bypass Final Solution Manager?
Bypass, vascular occlusions and narrowings are opened for the moment, but vascular stiffness does not disappear as a result of surgical intervention. The operation prevents the patient from having a heart attack, dying suddenly, and being restricted from society due to drug dependence.
Patients should organize their lives after the operation, avoid harmful foods and beverages, and live a quality life by abandoning their bad habits.
Situations in which bypass is required as a result of reocclusion of the coronary arteries:
The patient's vascular structure is bad,
Performing the first surgery at an early age,
risk of atherosclerosis,
Not bridging all vessels in the first surgery,
Accompanying chronic diseases such as diabetes (diabetes) and kidney disease,
Continuing to smoke
It is the insufficient treatment of high cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
How Long Is the Recovery Process After Bypass Surgery?
The patient, who is released from the intensive care unit after the operation and whose respiratory device is removed, starts exercises with the help of a physiotherapist to remove the sputum accumulated in the bronchi during the operation. The patient needs to stay in the hospital for four to seven days. If everything is normal at the end of this period, the patient is discharged.
One week later, the patient is called for control again. During the visit to the outpatient clinic, the general condition of the patient is observed, his complaints are evaluated, and his medications are rearranged when necessary. In the presence of accompanying diseases such as obesity, hypertension, diabetes, the patient is provided with a cardiologist for comprehensive follow-up.
The patient may need to use compression stockings. During the first phase of the recovery period, he should stay at home, but move without being tied to the bed.
It is possible to return to normal life at the end of one month after the surgery at the earliest. During this period, the patient may encounter problems such as not being able to turn sideways and not being able to drive, and full recovery occurs after six months.
The patient recovers completely when the cut bone and thorax heal during the operation. All kinds of activities that a normal person would do, work can be continued, a car can be used.
 How to Live After Surgery?
How to Live After Surgery?
Preoperative physicians often find it difficult to change their patients' lifestyles. After the operation, patients who become aware of the bypass operation and the severity of the disease apply the recommendations more carefully.
Things to pay attention:
If the patient smokes, he should definitely quit immediately,
Avoid doing heavy sports
Should lose excess weight with a strict diet under the control of a doctor,
He should be very careful about his sleep pattern.
After the surgery, the patient should take part in daily life as much as possible, use drugs regularly, pay attention to his diet, and use the recommended drugs.
Regularly attending rehabilitation sessions after bypass is very effective in overcoming psychological trauma for patients who want to return to their old lives. Since sudden changes in the heart rate can cause heart problems, dangerous combat sports that use weights and have a very intense tempo should be avoided.
Swimming can be applied because it is a sport that works all the muscles in the body and can also do breathing exercises. If possible, regular nature walks should be made in the open and fresh air. Activities such as table tennis and dance that can be done with the partner also contribute to the health of the patient and provide socialization.
Regular post-operative cardiology examinations should be done.
Regular Check-Up is important in early diagnosis of all diseases, especially possible vascular occlusions.