
Intervention Radiology makes use of applications for use in almost every organ in trendy, fashionable (Ultra, MR and Angio) guidance, and it is a science that uses different and technical techniques apart from a science for use.
Interventional Radiology operations are targeted diagnosis and operations; This success rate is high. Work-related side-effect, more customer-application-related. Interventional Radiology applications; traffic control will be done for major surgical interventions and more. Flat writes. stay short
Interventional radiological procedures, unlike other methods, are reproducible procedures. At the same time, for therapeutic surgery or therapeutic use, apply from a single center for you.
Interventional Radiology procedures, starting with preparations to embark on an organ or educational journey, to travel in close proximity to a cruise.
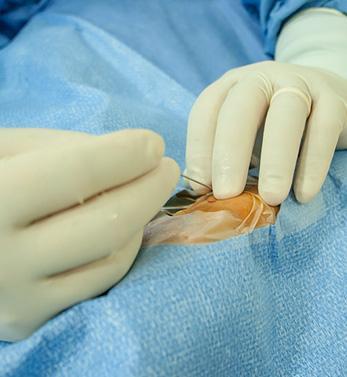
 1. Percutaneous Biopsies: Biopsies are performed and samples are taken from lesions in various tissues by applying local anesthesia, accompanied by imaging. In this way, the characters of the lesions are understood (fine needle aspiration biopsy and thick needle biopsy).
1. Percutaneous Biopsies: Biopsies are performed and samples are taken from lesions in various tissues by applying local anesthesia, accompanied by imaging. In this way, the characters of the lesions are understood (fine needle aspiration biopsy and thick needle biopsy).
2. Percutaneous abscess and collection drainages: Imaging of abscesses (inflammatory fluid) and collections (non-inflammatory body fluids) in the abdominal cavity and chest cavity with specially produced thin tube-like instruments called catheters, under local anesthesia (usually US and CT) guided unloading.
3.Percutaneous simple cyst and hydatid cyst treatments: Simple cystic structures originating from the tissues in the abdominal and thoracic cavities or cysts caused by parasites are evacuated. For example, hydatid cyst disease, which is said to be transmitted from cats and dogs among the people, is treated with interventional radiological techniques developed without surgery.
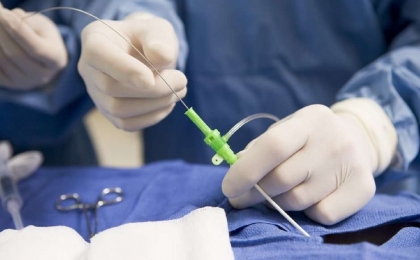
4.Percutaneous biliary drainage and biliary stent placement procedures: In case of obstruction of the bile ducts by tumor or other reasons, jaundice is encountered. In this case, the bile fluid is taken out of the body through the catheter. Sometimes, a balloon expansion process or a metallic tube called a “stent” is placed in the narrow/occluded area in the biliary system, allowing the bile flow to pass smoothly into the small intestine, where it should normally flow within the body.
5.Percutaneous cholecystostomy: Condensed and inflamed bile in the gallbladder is emptied out of the gallbladder with the help of a catheter in patients whose gallbladder cannot be surgically removed or who cannot be operated for a while.
6.Percutaneous nephrostomy: In cases where there is an obstacle in front of the urinary tract and the urine accumulates in the renal collecting system and causes enlargement of the kidney, the urine is taken out with special catheters and thus the kidney is prevented from being damaged.
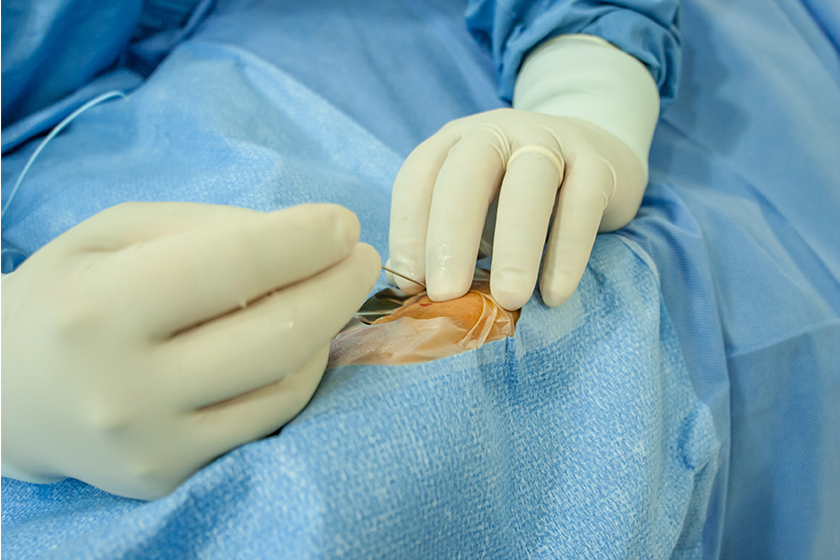
7.Percutaneous double-J stent placement: In patients with stenosis between the kidney and the bladder (bladder), who cannot be operated on, a double-J stent is placed between the kidney and the bladder to ensure continuous urine flow.
8.Percutaneous gastrostomy: In patients who cannot take food by mouth, a catheter is inserted through the skin into the stomach, accompanied by imaging, and the patient is fed from the stomach.
9. Percutaneous celiac ganglion blockade: In order to reduce pain in cancer patients or to reduce the amount of painkillers needed by the patient, pain treatment is applied by administering drugs to pain centers in the abdomen, accompanied by imaging methods.
10.Percutaneous tumor ablation (RFA and microwave burning): In cancer patients, tumors are controlled by burning them with high heat. This procedure is applied in primary (own) and secondary (spread of the tumor in another region) tumors of the liver and lung, kidney and some bone tumors. It is an important method in the treatment of cancer patients.
11. Vertebroplasty, kyphoplasty: Compression fractures may occur in the vertebral bones (vertebra bones) in cases such as osteoporosis and hemangioma. Reinforcing bone cement is given by inserting a needle into the collapsed bone. With this procedure, further damage to bone integrity and surrounding tissues is prevented.