
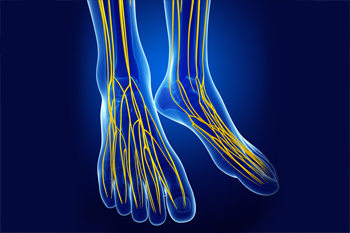
Damage to several of the nerves that form part of the peripheral nervous system at the same time is called polyneuropathy. In polyneuropathy, which is a disease that causes the nerves in the body to lose their function, neurological losses occur. The nervous system consists of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The peripheral nervous system is a nerve network that carries nerve roots, nerve tangles (plexuses) from the spinal cord, and impulses to the limbs and organs by peripheral nerves. The deterioration in nerves caused by this problem usually starts at the farthest end of the brain. The picture worsens due to loss of sensation that starts in the toes and extends upwards, and decreases in movement in the foot and hand muscles. Poly means multiplicity, neuro nerves, paw means damage. The incidence of polyneuropathy increases with age.
What Causes Polyneuropathy?
There are many underlying causes of the formation of polyneuropathy. One of the most common causes is diabetes. In addition, polyneuropathy can be seen in other metabolic, infectious and genetic diseases. In addition, various causes such as excessive alcohol consumption, chemotherapy drugs used in the treatment of cancer patients, cancer, infection, kidney and liver failure, and heavy metal poisoning can cause polyneuropathy.
What Are the Symptoms of Polyneuropathy?
Patients with polyneuropathy may have numbness, felting, burning, numbness or pain in the hands and/or feet.
These patients also have symptoms related to muscle strength, such as weakness in the hands and feet, gait disturbance, and inability to make fists.
There may be muscle wasting, delayed healing wounds, shedding of arm or leg hair, deformation in hands and feet, changes or ruptures in nails in the affected areas.
In patients with advanced polyneuropathy, wounds similar to bedsores and even gangrene may develop on the feet.
Diagnosing Polyneuropathy?
The diagnosis of polyneuropathy is made by the patient's complaints, clinical examination, laboratory tests and EMG (electromyography) test. EMG is an indispensable diagnostic method in the diagnosis of polyneuropathy. In this method, the thickness of the peripheral nerves, whether the nerve sheath is damaged, and whether the electrical current of the nerve is normal is evaluated by connecting cables to the patient's arms and legs and giving low-dose electrical stimulation. When necessary, the condition of the muscles is evaluated by using a needle during the EMG test for differential diagnosis in polyneuropathy patients.
Treatment of Polyneuropathy?
Treatment of polyneuropathy is carried out depending on the underlying causes. Since the most common type of polyneuropathy we see is related to diabetes, it is important to keep blood sugar under control first. In case of diabetes, it is recommended to use pain relievers and drugs that can repair nerve damage, if necessary, for the patient's complaints. Similarly, the polyneuropathies we see in chronic renal failure are due to metabolic causes and toxic substances accumulating in the body. Medications given to remove these substances from the body and, if necessary, dialysis contribute to the recovery of polyneuropathy. Unfortunately, there is no effective treatment for genetic polyneuropathies and most of the treatments are still in the experimental stage. Here, patient-specific physical therapy and symptomatic treatment can be applied to reduce their complaints.