




The uterus, which is one of the female reproductive organs, is not fixed in its location since it is an organ with limited mobility. On the contrary, it is suspended in this area thanks to the pelvic muscles and connective tissues. Uterine prolapse, or in other words, uterine prolapse is the condition where the uterus hangs down from where it should normally be. Pelvic muscles and connective tissues relax due to reasons such as normal birth, multiple pregnancy, insufficient estrogen hormone and old age. Due to this relaxation, with the effect of gravity, the uterus; it hangs down, that is, into the vagina. This sagging may also be so advanced that it is visible from the outside of the vagina. Although uterine prolapse does not require treatment in every case, it can be treated if it interferes with the person's daily activities.
As it can be seen in women of all ages, its incidence increases with factors such as advanced age or the number of births. Age, birth, some diseases, chronic constipation, heavy lifting and the effect of daily life, weakening of these muscles and sagging of the uterus downwards are called uterine prolapse. Uterine prolapse, a disease that increases with age in women, is one of the most common gynecological diseases. The uterus, which is one of the female reproductive organs, is not fixed in its location since it is an organ with limited mobility. Uterus; A reproductive organ in women, which is firmly attached to the pelvis and firmly attached to the pelvic floor muscles, hangs on this area. Uterine prolapse may show different symptoms depending on the stage. Although uterine prolapse does not require treatment in every case, it should be treated if it prevents the person's daily activities. With the effect of uterine prolapse, sagging also occurs in the large intestine and urinary bladder. It should be kept in mind that uterine prolapse is not alone and most likely affects neighboring organs negatively. For this reason, it is a disease that should be taken seriously and treated.
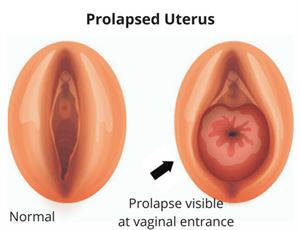
Stages of Uterine Prolapse
Uterine prolapse disease is examined in four stages as mild, moderate and very severe. The severity of the sagging in the vagina determines the stage of the disease. In the first stage of the disease, the symptoms are usually not noticed and are mild. Most women do not care about mild pain in the groin and vagina and do not consult a doctor. For this reason, the probability of recognizing and diagnosing the disease in the first stage is low. In the majority of patients, symptoms are noticed in the second stage. The patient's hand feels full, he feels downward pressure, and it begins to be understood that there is something strange. In the third stage, sagging organs and skin are noticed. The rate of aches and pains is higher. Skin fragments that come out are irritated by friction. The main discomfort and decrease in the quality of life begin to be seen in this process. In the fourth, the last stage, the uterus and urinary bladder come out clearly. Irritations caused by friction in the third stage turn into wounds. Prolapse of the uterus also damages the organs next to it. As in any disease, early diagnosis is of great importance in uterine prolapse.
What Causes Uterine Prolapse?
There are many reasons for uterine prolapse. One of the most important reasons is the age factor. Although it can be seen in young ages, it is more common in older ages. With the effect of aging, as in other organs of the body, the skin sags with the effect of gravity, and this is also seen in the uterus. This age-related reaction of the body is quite natural. At the same time, the estrogen hormone decreases after menopause, and after the decreasing estrogen hormone, shrinkage and weakening will occur in these tissues.
One of the most well-known causes of uterine prolapse is normal births. Difficult delivery can contribute to uterine prolapse. Along with prolonged delivery, excessive straining and similar factors may contribute to uterine prolapse. In addition, multiple pregnancies such as twin triplets, multiple births, and births of more than four kilograms can cause this discomfort. In addition, the use of vacuum during delivery can increase the degree of uterine prolapse.
In another reason, being overweight is also known as one of the reasons for uterine prolapse. High pressure from top to bottom causes uterine prolapse. Parallel to excess weight, muscle weakness also causes uterine sagging due to the lack of exercise habits in the person. In addition, excessive coughing and straining that increase intra-abdominal pressure can also cause this problem. For this reason, problems that cause coughing, such as chronic lung diseases, or factors that increase intra-abdominal pressure, such as constipation, trigger uterine prolapse. This problem is more common in women with these and similar disorders.
In addition to all these, previous pelvic operations and genetic factors may also cause uterine prolapse. Women with a family history of uterine prolapse due to genetic predisposition should be more careful and attentive. Routine check-ups are very important for these people.
The complaints of uterine prolapse are also more common in women who frequently lift heavy loads due to their occupation or housework. For this reason, care should be taken not to lift too heavy or push or pull while doing housework. The same care should be taken in the workplace and excessive weight should not be put under it. If heavy lifting is required for the job, the right bending and lifting methods should be chosen.
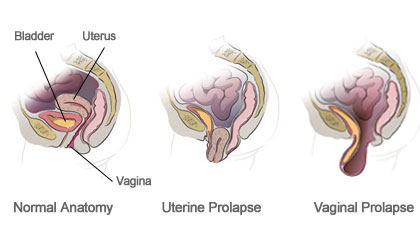
Treatment of Uterine Prolapse
Uterine prolapse treatment is planned according to the current severity of the prolapse and the patient's complaints.
Mild cases of uterine prolapse do not require surgical treatment. However, in order not to increase the severity of sagging, the physician may recommend Kegel exercises (pelvic floor exercises) to the person. In addition, if the person has chronic cough, chronic constipation, the patient is informed about the treatment of diseases such as chronic cough and chronic constipation and not to lift heavy. Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles does not improve the cases of uterine prolapse in the early period, but it can prevent the severity of the disease, that is, the sagging of your uterus further. In addition, the patient is informed about the treatment of diseases such as chronic cough, chronic constipation and not lifting heavy weights, if any.
If the situation is more advanced than mild uterine prolapse and surgical intervention cannot be performed for any reason (for example, if the patient refuses to have surgery or does not have a child yet), the use of an apparatus called pessary, which is placed in the vagina and provides relief by supporting the sagging organ, may be preferred. The pessary, which comes in a wide variety of shapes and sizes, is selected according to the patient's condition. It may take some trial and error to see if the pessary used is suitable for the person. Although it is not valid for all types, it is possible to experience sexual intercourse while the apparatus is in place.
If the uterine prolapse is very advanced, surgical treatment may be required.
Uterine Prolapse Surgery
The decision of which type of surgery to perform uterine prolapse is made specifically for the patient. The severity of the sagging, health status, whether the woman has or wants to have children, as well as her history are the main determinants in determining which type of treatment will be given.
Depending on the severity of the uterine prolapse, the surgical treatment option can be applied. The aim of the surgical intervention is to repair the pelvic floor tissues, but if the repair cannot be performed, it is also possible to remove the uterus.
Tissue repair can be done by reaching the uterus with incisions/holes made from both the vaginal canal or the abdomen. Which method to use depends on the patient's current condition and the surgeon's decision. With uterine surgery, it is aimed to strengthen the weakened pelvic floor. Here, weakened pelvic tissues are strengthened with tissues taken from different parts of the person or with synthetic material, namely mesh.
Abdominal, laparoscopic, robotic and vaginal approaches are surgical approaches in uterine prolapse surgery. The approach adopted in surgeries is variable as each woman's story is different. For this reason, the most appropriate method for the person is determined after the doctor examines the patient in detail. The success of the surgery also varies according to the preferred method. Long-term improvements are observed in both the abdominal approach and the vaginal approach.
If the causes of uterine prolapse continue, there is a risk of recurrence of the same situation. For example, if the uterus has prolapsed due to constipation and the constipation continues after the surgery, there is a possibility of recurrence. Therefore, it is important to investigate and prevent the underlying causes.
In patients who are at an advanced age or whose sexual life has been completed, the method of closure of the uterus, namely colpeclesis operation, may also be preferred. In this treatment method, the uterus is pushed upwards piece by piece and recovered. After this procedure, the urinary bladder and large intestine are supported along with the uterus. This is usually the first treatment method recommended for patients of advanced age and in whom the operation is risky. The complication rate after this surgery is very low.
Which of these treatment methods is suitable for the person is decided together with the patient according to the severity of uterine prolapse, the person's complaints, and whether or not he is planning a pregnancy. If uterine prolapse is not treated, its severity may increase. The prolapse of the uterus from the vagina can cause many different health problems.
A person suffering from uterine prolapse should definitely undergo a gynecological examination. Many patients may not have symptoms in the first stage. From the moment the symptoms begin to appear, the person should definitely see a doctor. If symptoms are mild, treatment may not be needed. Some women do not care about these symptoms and do not consult a doctor. In this case, the transition to advanced stages accelerates. Some women are also hesitant to go to the doctor depending on the situation or environment they are in. This accelerates the progression of the disease to other stages. A suitable treatment method is determined for the patient who goes to the doctor and is examined in detail. This method varies according to the stage of uterine prolapse, age or preference of the person.
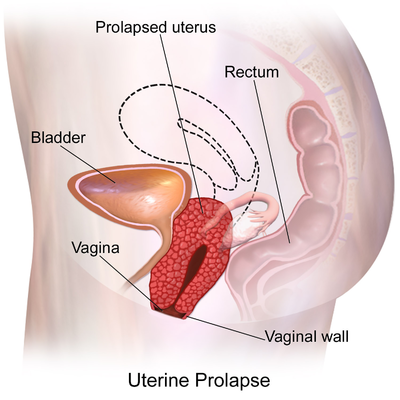
Sacrocervicopexy – Sacrocolpopexy – Sacrouteropexy – What is sacrouteropexy?
If a patient with uterine prolapse does not want the uterus to be removed and does not have enough children, then an operation is performed to suspend the uterus with a prolene patch (mesh) to the bone called the sacrum with a laparoscopic-closed but open surgery (Sacrohysteropexy - Sacroteropexy - Sacrocervicopexy) Prolapse of the urinary bladder - Cystocele and breech sagging – If there is a rectocele, sagging of the urinary bladder and breech; If there is, Cystocele and rectocele Repair is also added to this operation. If there is also stress type urinary incontinence when coughing, sneezing and straining, TOT (urinary incontinence) operation is added to the preferred laparoscopic Sacrohysteropexy – Sacrouteropexy – Sacrocervicopexy closed surgery.
In some patients, after the uterus removal surgery, the vaginal dome sags over the years. In this case, the patients undergo laparoscopic-closed surgery and suspend the vaginal dome (colpos-cuff) to the bone called the sacrum with prolene mesh, which is called laparoscopic sacrocolpopexy surgery.
Laparoscopic Sacrohysteropexy – Sacrouteropexy – Sacrocervicopexy – What Should Be Done After Sacrocolpopexy Surgery?
After the surgery, your doctor will tell you what to do or what not to do according to the surgery. You do not need to have stitches removed after discharge because the stitches will fall off on their own in an average of 20 days.
It is recommended that you lie in the bathtub for 10 days and do not enter the sea or pool. and 1.5 – 2 months relationship status is prohibited.